手写Vue-router核心原理
核心原理
什么是前端路由?
在 Web 前端单页应用 SPA(Single Page Application)中,路由描述的是 URL 与 UI 之间的映射关系,这种映射是单向的,即 URL 变化引起 UI 更新(无需刷新页面)。如何实现前端路由?
要实现前端路由,需要解决两个核心:
1. 如何改变 URL 却不引起页面刷新?
2. 如何检测 URL 变化了?下面分别使用 hash 和 history 两种实现方式回答上面的两个核心问题。
hash 实现
hash 是 URL 中 hash (#) 及后面的那部分,常用作锚点在页面内进行导航,改变 URL 中的 hash 部分不会引起页面刷新
通过 hashchange 事件监听 URL 的变化,改变 URL 的方式只有这几种:
- 通过浏览器前进后退改变 URL
- 通过<a>标签改变 URL
- 通过window.location改变URL
history 实现
history 提供了 pushState 和 replaceState 两个方法,这两个方法改变 URL 的 path 部分不会引起页面刷新
history 提供类似 hashchange 事件的 popstate 事件,但 popstate 事件有些不同:
- 通过浏览器前进后退改变 URL 时会触发 popstate 事件
- 通过pushState/replaceState或<a>标签改变 URL 不会触发 popstate 事件。
- 好在我们可以拦截 pushState/replaceState的调用和<a>标签的点击事件来检测 URL 变化
- 通过js 调用history的back,go,forward方法课触发该事件
所以监听 URL 变化可以实现,只是没有 hashchange 那么方便。
二、原生js实现前端路由
1 .基于 hash 实现
<html lang="en">
<body>
<ul>
<ul>
<!-- 定义路由 -->
<li><a href="#/home">home</a></li>
<li><a href="#/about">about</a></li>
<!-- 渲染路由对应的 UI -->
<div id="routeView"></div>
</ul>
</ul>
</body>
<script>
let routerView = routeView
window.addEventListener('hashchange', ()=>{
let hash = location.hash;
routerView.innerHTML = hash
})
window.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', ()=>{
if(!location.hash){//如果不存在hash值,那么重定向到#/
location.hash="/"
}else{//如果存在hash值,那就渲染对应UI
let hash = location.hash;
routerView.innerHTML = hash
}
})
</script>
</html>
解释下上面代码,其实很简单:
我们通过a标签的href属性来改变URL的hash值(当然,你触发浏览器的前进后退按钮也可以,或者在控制台输入window.location赋值来改变hash) 我们监听hashchange事件。一旦事件触发,就改变routerView的内容,若是在vue中,这改变的应当是router-view这个组件的内容 为何又监听了load事件?这时应为页面第一次加载完不会触发 hashchange,因而用load事件来监听hash值,再将视图渲染成对应的内容。
2. 基于 history 实现
<html lang="en">
<body>
<ul>
<ul>
<li><a href='/home'>home</a></li>
<li><a href='/about'>about</a></li>
<div id="routeView"></div>
</ul>
</ul>
</body>
<script>
let routerView = routeView
window.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', onLoad)
window.addEventListener('popstate', ()=>{
routerView.innerHTML = location.pathname
})
function onLoad () {
routerView.innerHTML = location.pathname
var linkList = document.querySelectorAll('a[href]')
linkList.forEach(el => el.addEventListener('click', function (e) {
e.preventDefault()
history.pushState(null, '', el.getAttribute('href'))
routerView.innerHTML = location.pathname
}))
}
</script>
</html>
解释下上面代码,其实也差不多:
我们通过a标签的href属性来改变URL的path值(当然,你触发浏览器的前进后退按钮也可以,或者在控制台输入history.go,back,forward赋值来触发popState事件)。这里需要注意的就是,当改变path值时,默认会触发页面的跳转,所以需要拦截 <a>标签点击事件默认行为, 点击时使用 pushState 修改 URL并更新手动 UI,从而实现点击链接更新 URL 和 UI 的效果。我们监听popState事件。一旦事件触发,就改变routerView的内容。 load事件则是一样的
有个问题:hash模式,也可以用history.go,back,forward来触发hashchange事件吗?
A:也是可以的。因为不管什么模式,浏览器为保存记录都会有一个栈。
三、基于Vue实现VueRouter##
我们先利用vue-cli建一个项目
删除一些不必要的组建后项目目录暂时如下:
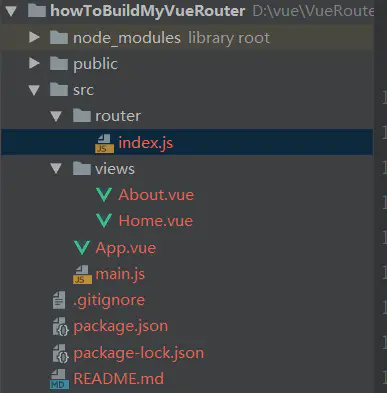
我们主要看下App.vue,About.vue,Home.vue,router/index.js
代码如下:
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<div id="nav">
<router-link to="/home">Home</router-link> |
<router-link to="/about">About</router-link>
</div>
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
router/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import Home from '../views/Home.vue'
import About from "../views/About.vue"
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const routes = [
{
path: '/home',
name: 'Home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'About',
component: About
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
mode:"history",
routes
})
export default router
Home.vue
<template>
<div class="home">
<h1>这是Home组件</h1>
</div>
</template>
复制代码About.vue
<template>
<div class="about">
<h1>这是about组件</h1>
</div>
</template>
复制代码现在我们启动一下项目。看看项目初始化有没有成功。

ok,没毛病,初始化成功。
现在我们决定创建自己的VueRouter,于是创建myVueRouter.js文件
目前目录如下
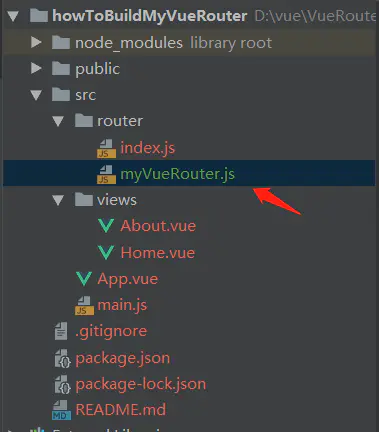
再将VueRouter引入 改成我们的myVueRouter.js
//router/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from './myVueRouter' //修改代码
import Home from '../views/Home.vue'
import About from "../views/About.vue"
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const routes = [
{
path: '/home',
name: 'Home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'About',
component: About
}
];
const router = new VueRouter({
mode:"history",
routes
})
export default router
四、剖析VueRouter本质
先抛出个问题,Vue项目中是怎么引入VueRouter。
安装Vuex,再通过 import VueRouter from 'vue-router'引入先 const router = new VueRouter({...}),再把router作为参数的一个属性值,new Vue({router})通过Vue.use(VueRouter) 使得每个组件都可以拥有store实例
从这个引入过程我们可以发现什么?
我们是通过new VueRouter({...})获得一个router实例,也就是说,我们引入的VueRouter其实是一个类。
所以我们可以初步假设
class VueRouter{
}
我们还使用了Vue.use(),而Vue.use的一个原则就是执行对象的install这个方法
所以,我们可以再一步 假设VueRouter有有install这个方法。
到这里,你能大概地将VueRouter写出来吗?
很简单,就是将上面的VueRouter导出,如下就是myVueRouter.js
//myVueRouter.js
class VueRouter{
}
VueRouter.install = function () {
}
export default VueRouter
五、分析Vue.use
Vue.use(plugin);
(1)参数
{ Object | Function } plugin
(2)用法
安装Vue.js插件。如果插件是一个对象,必须提供install方法。如果插件是一个函数,它会被作为install方法。调用install方法时,会将Vue作为参数传入。install方法被同一个插件多次调用时,插件也只会被安装一次。
(3)作用
注册插件,此时只需要调用install方法并将Vue作为参数传入即可。但在细节上有两部分逻辑要处理:
1、插件的类型,可以是install方法,也可以是一个包含install方法的对象。
2、插件只能被安装一次,保证插件列表中不能有重复的插件。
(4)实现
Vue.use = function(plugin){
const installedPlugins = (this._installedPlugins || (this._installedPlugins = []));
if(installedPlugins.indexOf(plugin)>-1){
return this;
}
<!-- 其他参数 -->
const args = toArray(arguments,1);
args.unshift(this);
if(typeof plugin.install === 'function'){
plugin.install.apply(plugin,args);
}else if(typeof plugin === 'function'){
plugin.apply(null,plugin,args);
}
installedPlugins.push(plugin);
return this;
}
1、在Vue.js上新增了use方法,并接收一个参数plugin。
2、首先判断插件是不是已经别注册过,如果被注册过,则直接终止方法执行,此时只需要使用indexOf方法即可。
3、toArray方法我们在就是将类数组转成真正的数组。使用toArray方法得到arguments。除了第一个参数之外,剩余的所有参数将得到的列表赋值给args,然后将Vue添加到args列表的最前面。这样做的目的是保证install方法被执行时第一个参数是Vue,其余参数是注册插件时传入的参数。
4、由于plugin参数支持对象和函数类型,所以通过判断plugin.install和plugin哪个是函数,即可知用户使用哪种方式祖册的插件,然后执行用户编写的插件并将args作为参数传入。
5、最后,将插件添加到installedPlugins中,保证相同的插件不会反复被注册。(~~让我想起了曾经面试官问我为什么插件不会被重新加载!!!哭唧唧,现在总算明白了)
第三点讲到,我们把Vue作为install的第一个参数,所以我们可以把Vue保存起来
//myVueRouter.js
let Vue = null;
class VueRouter{
}
VueRouter.install = function (v) {
Vue = v;
};
export default VueRouter
然后再通过传进来的Vue创建两个组件router-link和router-view
//myVueRouter.js
let Vue = null;
class VueRouter{
}
VueRouter.install = function (v) {
Vue = v;
console.log(v);
//新增代码
Vue.component('router-link',{
render(h){
return h('a',{},'首页')
}
})
Vue.component('router-view',{
render(h){
return h('h1',{},'首页视图')
}
})
};
export default VueRouter
我们执行下项目,如果没报错,说明我们的假设没毛病。

六、完善install方法
install 一般是给每个vue实例添加东西的
在这里就是给每个组件添加$route和$router。
$route和$router有什么区别?
A:
$router是VueRouter的实例对象,$route是当前路由对象,也就是说$route是$router的一个属性 注意每个组件添加的$route是是同一个,$router也是同一个,所有组件共享的。
看下VueRouter的完整代码吧
//myVueRouter.js
let Vue = null;
class HistoryRoute {
constructor(){
this.current = null
}
}
class VueRouter{
constructor(options) {
this.mode = options.mode || "hash"
this.routes = options.routes || [] //你传递的这个路由是一个数组表
this.routesMap = this.createMap(this.routes)
this.history = new HistoryRoute();
this.init()
}
init(){
if (this.mode === "hash"){
// 先判断用户打开时有没有hash值,没有的话跳转到#/
location.hash? '':location.hash = "/";
window.addEventListener("load",()=>{
this.history.current = location.hash.slice(1)
})
window.addEventListener("hashchange",()=>{
this.history.current = location.hash.slice(1)
})
} else{
location.pathname? '':location.pathname = "/";
window.addEventListener('load',()=>{
this.history.current = location.pathname
})
window.addEventListener("popstate",()=>{
this.history.current = location.pathname
})
}
}
createMap(routes){
return routes.reduce((pre,current)=>{
pre[current.path] = current.component
return pre;
},{})
}
}
VueRouter.install = function (v) {
Vue = v;
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate(){
if (this.$options && this.$options.router){ // 如果是根组件
this._root = this; //把当前实例挂载到_root上
this._router = this.$options.router;
Vue.util.defineReactive(this,"xxx",this._router.history)
}else { //如果是子组件
this._root= this.$parent && this.$parent._root
}
Object.defineProperty(this,'$router',{
get(){
return this._root._router
}
});
Object.defineProperty(this,'$route',{
get(){
return this._root._router.history.current
}
})
}
})
Vue.component('router-link',{
props:{
to:String
},
render(h){
let mode = this._self._root._router.mode;
let to = mode === "hash"?"#"+this.to:this.to
return h('a',{attrs:{href:to}},this.$slots.default)
}
})
Vue.component('router-view',{
render(h){
let current = this._self._root._router.history.current
let routeMap = this._self._root._router.routesMap;
return h(routeMap[current])
}
})
};
export default VueRouter



